Latrodectus: A New Malware Emerges in Phishing Campaigns
Key Points
- Latrodectus, an evolution of the IcedID loader, was discovered in malicious email campaigns since November 2023.
- Researchers at Proofpoint and Team Cymru documented Latrodectus’ unstable and experimental capabilities.
- IcedID, a modular banking trojan, was initially designed to steal financial information from infected computers. Over time, it became more sophisticated, adding evasion and command execution capabilities.
- Latrodectus has acted as a loader that can deliver other types of malware, including ransomware, onto infected systems.
- Researchers believe that the developers of IcedID created Latrodectus after noting they shared infrastructure and operational overlaps.
- Initial access brokers (TA577 and TA578) who previously distributed IcedID have now begun to distribute Latrodectus in phishing campaigns.
- Latrodectus performs various sandbox evasion checks before running on the device to avoid detection and analysis by security researchers.
- The malware’s infrastructure is separated into two distinct tiers that follow a dynamic operation approach regarding campaign involvement and lifespan.
Background
Security experts have discovered a new malware called Latrodectus, which has been propagated through email phishing campaigns since late November 2023. Proofpoint and Team Cymru’s joint investigation identifies Latrodectus as a downloader with sandbox evasion capabilities that can download payloads and execute arbitrary commands. Evidence suggests that it may be tied to the same threat actors that utilized IcedID malware to distribute more malware through initial access brokers (IABs).
Latrodectus is primarily related to two IABs, TA577 (Water Curupira) and TA578, and it has been used almost entirely by TA578 in email threat campaigns since mid-January 2024. TA578, which has been active since May 2020, has been linked to a variety of malware deployments, including Ursnif, IcedID, KPOT Stealer, and Buer Loader. It uses contact forms on websites to convey legal threats over claimed copyright infringement to target organizations.
Consequences
Infections with Latrodectus are dangerous. Their main objective is to establish a backdoor so that thieves can upload more malware. This has been noted to consist of:
Malware that steals information: This type of software is made to steal private information, such as bank account details, login passwords, and corporate data.
Trojan Programs: Trojan programs are malicious software that allows for remote access control, potentially granting hackers total access to your computer.
Businesses may have extensive repercussions from these attacks, including network intrusions, data breaches, and even collaborations with ransomware gangs.
Analysis
Sandbox Evasion
The trojan starts by resolving bulk APIs for multiple functions. After resolving all functions to global pointers, the malware performs virtualization checks to guarantee that it is operating in an appropriate environment. It checks the host for the following features because the absence of these properties usually indicates that the sample is being executed in a sandbox:
- If Windows 10 or newer, have at least 75 running processes.
- If older than Windows 10, have at least 50 ongoing processes.
- Ensure the 64-bit program is operating on a 64-bit host and that the host has a valid MAC address.
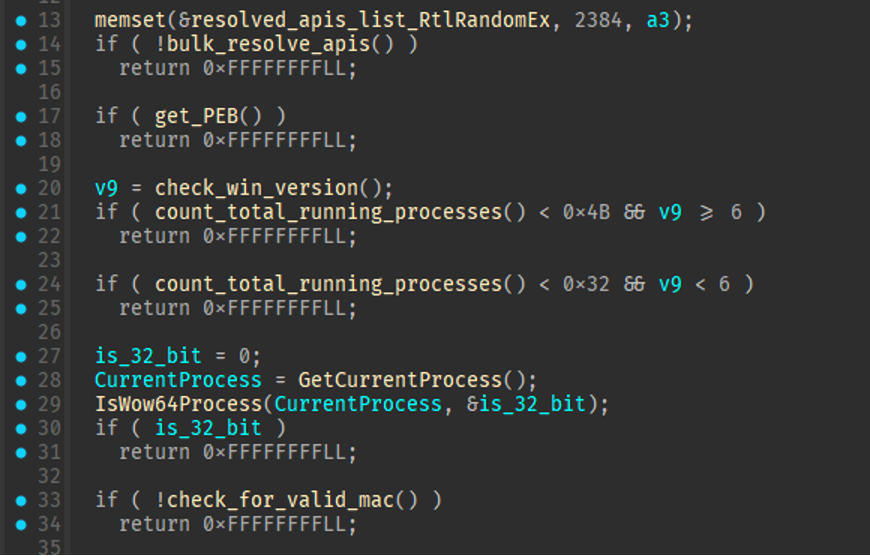
Fig. Sandbox checks
Since the malware’s identification, all samples investigated have consistently registered a mutex called “runnung” [sic]. If the mutex already exists, it indicates that the host already has an infection, and the malware will exit, causing the new infection to cease.
Latrodectus generates a bot ID for each unique host where the malware is installed. The bot ID, like IcedID, is generated from the host’s serial ID.
Network communication
Latrodectus, like IcedID, delivers registration information via a POST request with fields that are HTTP parameters concatenated together.
If the bot is coming from an IP address that is not blocked and has passed all other filters, a response will be sent, which, when encoded and decrypted with the global key “12345”, yields a list of commands to be parsed by the first command handler.
This response, when base64 decoded and RC4 decrypted with the global key “12345”, will show the following:
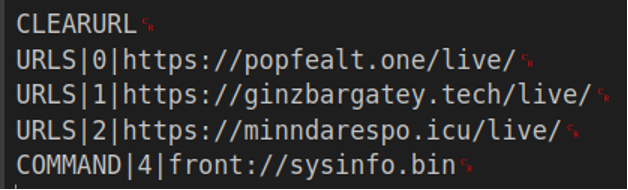
Fig. Decrypted command response
The response is parsed based on the significant keywords. The URLs keyword replaces the C2s in the sample with the three specified in the command. When “COMMAND” is handled, a second-layer command handler is activated.
List of supported commands:
| Enum name | Enum value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cmd_get_desktop_items | 2 | Get the filenames of files on the desktop |
| cmd_get_proclist | 3 | Get the list of running processes |
| cmd_get_sysinfo | 4 | Send additional system information |
| cmd_exec_exe | 12 | Execute executable |
| cmd_exec_dll | 13 | Execute DLL with given export |
| cmd_exec_cmd | 14 | Pass string to cmd and execute |
| cmd_update | 15 | Update the bot and trigger a restart |
| cmd_kill | 17 | Shutdown the running process |
| cmd_run_icedid | 18 | Download bp.dat and execute |
| cmd_change_timing | 19 | Set a flag to reset the communications timing |
| cmd_reset_counter | 20 | Reset the counter variable used in communications |
IOCs
URLs
hxxps://mazdakrichest[.]com/live/
hxxps://riverhasus[.]com/live/
hxxp://162[.]55[.]217[.]30/gRMS/0[.]6395541546258323[.]dat
hxxp://157[.]90[.]166[.]88/O3ZlYNW/0[.]7797109211833805[.]dat
hxxp://128[.]140[.]36[.]37/cQtDIo/0[.]43650426987684443[.]dat
hxxps://peermangoz[.]me/live/
hxxps://aprettopizza[.]world/live/
hxxps://nimeklroboti[.]info/live/
hxxps://frotneels[.]shop/live/
hxxps://hukosafaris[.]com/elearning/f/q/daas-area/chief/index[.]php
77[.]91[.]73[.]187:443
74[.]119[.]193[.]200:443
hxxps://arsimonopa[.]com/live
hxxps://lemonimonakio[.]com/live
hxxp://superior-coin[.]com/ga/index[.]php
hxxp://superior-coin[.]com/ga/m/6[.]dll
hxxps://fluraresto[.]me/live/
hxxps://mastralakkot[.]live/live/
hxxps://postolwepok[.]tech/live/
hxxps://trasenanoyr[.]best/live/
hxxps://miistoria[.]com/live
hxxps://plwskoret[.]top/live
hxxp://178[.]23[.]190[.]199:80/share/gsm[.]msi
hxxps://sluitionsbad[.]tech/live/
hxxps://grebiunti[.]top/live/
hxxp://5[.]252[.]21[.]207@80/share/escape[.]msi
hxxps://zumkoshapsret[.]com/live/
hxxps://jertacco[.]com/live/
hxxp://5[.]252[.]21[.]207/share/escape[.]msi
hxxp://95[.]164[.]3[.]171/share/cisa[.]msi
hxxps://scifimond[.]com/live/
hxxps://aytobusesre[.]com/live/
hxxps://popfealt[.]one/live/
hxxps://ginzbargatey[.]tech/live/
hxxps://minndarespo[.]icu/live/
hxxps://drifajizo[.]fun/live/
hxxp://sokingscrosshotel[.]com/share/upd[.]msi
hxxps://titnovacrion[.]top/live/
Hashes
Detection
rule lactrodectus {
strings:
$string_0 = { 488b4c2428 0fbe09 3bc1 7512 }
$string_1 = { c744242002000000 e9???????? 837c243406 7511 837c243801 750a }
$string_2 = { 8b00 488b4c2430 488b09 0fbe0401 48634c2404 488b542428 0fbe0c0a }
$string_3 = { eb43 41b901000000 448b442424 488b542428 488b4c2448 e8???????? }
$string_4 = { eb1f c744242000000000 4533c9 4533c0 }
$string_5 = { 488b4c2448 ff15???????? 89442444 837c244400 7502 eb11 }
$string_6 = { 488d8c0c60020000 ba02000000 486bd200 4803ca 448bc0 488b542420 e8???????? }
$string_7 = { 66c1ca08 0fb7d2 4c8b8424a0000000 450fb74006 6641c1c808 450fb7c0 4c8b8c24a0000000 }
$string_8 = { e8???????? b910000000 e8???????? 4889442448 488b442448 488b4c2450 488908 }
$string_9 = { 4889542410 48894c2408 4883ec78 c744243000000000 c744243400000000 488b942488000000 488d4c2448 }
condition:
7 of them and filesize < 148480
}
Recommendations
While Latrodectus is a serious concern, organizations can make efforts to reduce the risk:
- Patch Management: Updating operating systems and applications with the most recent security patches is critical for addressing known vulnerabilities that attackers may exploit.
- Endpoint Security Solutions: Implement strong endpoint security solutions capable of identifying and stopping harmful downloads and executions, such as Latrodectus.
- Employee Training: Educate staff on cybersecurity best practices, such as phishing awareness and how to recognize suspicious emails and attachments.
- Network segmentation: By restricting lateral movement within your network, you can limit the potential damage caused by an infected system.
- Email Scrutiny: Exercise extreme caution when responding to unsolicited emails, particularly if they appear to be a chain. Verify email addresses again and carefully examine any links or attachments before responding.
- Software Verification: If you’re unsure of the origins of a document, get in touch with the supposed sender through a different channel—like phone—to confirm its authenticity.